Oxygen | O2
Oxygen is a life-sustaining component of our atmosphere. It is almost 21% by volume of the air we breathe. It has no color, odor or taste.
Oxygen occurs more than any other element on our planet. Except for the noble gases Oxygen forms compounds with almost all chemical elements. It is in our streams, rivers, lakes and oceans.
In it’s pure state, Oxygen is highly combustible especially in it’s pure state. A great deal of the reactions necessitates the presence of water or are accelerated by a spark.
Oxygen has a low boiling/condensing point of -297.3°F (-183°C). The gas is roughly 1.1 times heavier than air and is slightly soluble in water and alcohol. Oxygen is a pale blue liquid a little heavier than water when it is below its boiling point.
It is the second largest volume industrial gas. Oxygen may be referred to as its chemical name O2, GOX or GO when delivered in gaseous form or LOX or LO when it’s in a cryogenic liquid form.
Oxygen is appreciated for its reactivity. It is used with air or instead of it to intensify the amount of oxygen for biological activity or combustion.
Oxygen has many uses in healthcare and industrial settings. It is used in steelmaking and metal refining and fabrication. It is used in petroleum processing, ceramic and glass manufacturing, pharmaceuticals and paper manufacturing. Environmental protection and effluent treatment plants benefit from the use of oxygen. In healthcare, it is used in hospitals, outpatient centers and individual homes.
Oxygen (O2) Applications and Uses:
- Multi-industrial uses
- Gas welding
- Gas cutting (must be high quality to ensure a clean cut)
- Metals Manufacturing
- Chemicals, Pharmaceuticals and Petroleum
- Glass and Ceramics Industry
- Pulp and Paper Manufacturing
- Health Care
- Environmental
- Miscellaneous Uses
- Underwater breathing
- Aquaculture
- Liquid oxygen is used in liquid fueled rockets
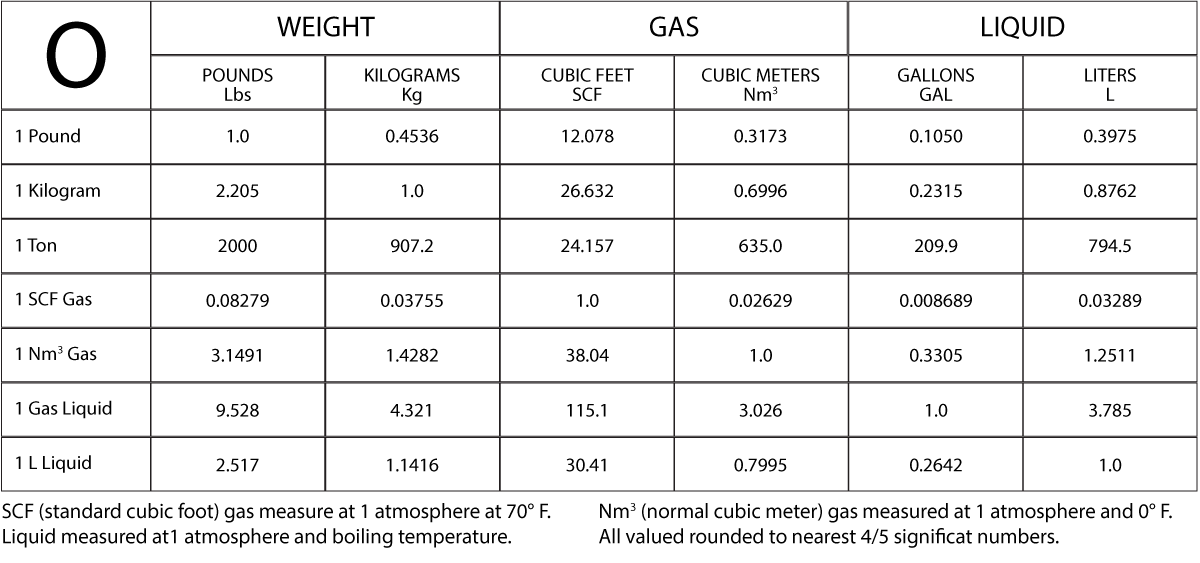
Turn phone to landscape for easier viewing of the chart.